HAIs
Latest News

CME Content


If you have ever watched a fibrin sheath progress to a thrombus on the surface of a catheter -- a process that initiates instantly upon entry into the bloodstream and proceeds quickly, often in just minutes -- you will understand why the presence of contaminating bacteria on the surface of a catheter is something to be rigorously avoided. The rapidly forming fibrin sheath encases such surface bacteria, both shielding them and facilitating biofilm formation.

Slips, trips, falls and sharps are widely recognized as potential occupational risks in the healthcare industry. However, there is another dangerous hazard that often goes unnoticed and underreported-splashes.

A UC Irvine research team will receive up to $5 million to further develop a bloodstream infection detection system that speeds up diagnosis times with unprecedented accuracy – allowing physicians to treat patients with potentially deadly ailments more promptly and effectively. The five-year federal award is part of a National Institute of Allergy & Infectious Diseases program to fund nine institutions that will create tools to identify certain pathogens that frequently cause infections in healthcare settings – especially those that are resistant to most antimicrobials.






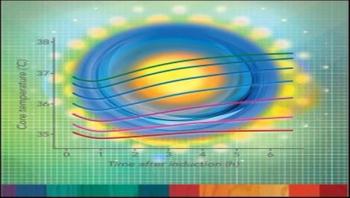




Sometimes the most commonly used tools for stopping infections are not quite enough to combat the ongoing struggle against hospital-acquired infections. As outlined in the recent Consumer Reports article, “Deadly hospital infections are still too common,” prevention measures such as hand hygiene, wound care and limiting use of central lines and urinary catheters are hugely important. But infection control can and should go far beyond these steps. One million Americans suffer from hospital-acquired infections each year – with a mortality rate of 100,000 per year and a price tag many times that, healthcare facilities must take advantage of every available tool to control and reduce the spread of disease.

This is a story about nursing education – both academic and clinical. It’s a powerful example of how one can impact the other, and how both can lead to a new evidence-based best practice that benefits patients and their providers. It’s also about nursing compassion, and a willingness to change a culture in order to prevent patient suffering.



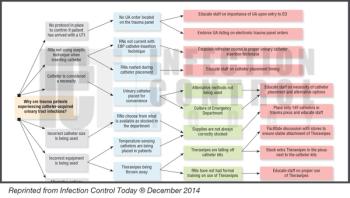
This is a story about nursing education – both academic and clinical. It’s a powerful example of how one can impact the other, and how both can lead to a new evidence-based best practice that benefits patients and their providers. It’s also about nursing compassion, and a willingness to change a culture in order to prevent patient suffering.




Two approaches to infection prevention that are being used in hospitals today bear continued scrutiny as multidrug-resistant organisms proliferate, emphasize experts writing in a recent commentary in the journal Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. Edward Septimus, MD, of the Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, and of Hospital Corporation of America in Nashville, Tenn. and his co-authors urge clinicians to carefully consider the clinical advantages and cost-related disadvantages to each strategy.



