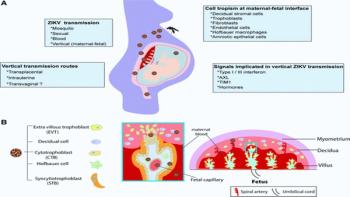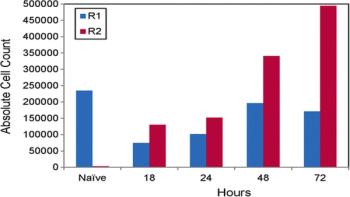
A new study of infection by a virus that causes brain inflammation and seizures in a mouse model has shown increased levels of complement component C3. The C3 was produced by immune cells in the brain called microglia within the first few days after infection. C3 showed the greatest increase in expression in the brain compared to a variety of other complement components, cytokines, chemokines, and antigens measured in the study that is published in Viral Immunology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers.