Videos
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Priya Nori, MD: “The immediate thing that the health care industry has to grapple with, even as COVID hopefully starts to settle down after the mass vaccination campaign … [will be] superbugs.”
Michael L. Millenson: “The CDC will pay more attention to infections. But there’s also an asterisk here. Will Congress continue to pay attention to infections? Will the administration’s budget continue to pay attention to infections? Will the media continue to pay attention to infections?”
Beau Wangtrakuldee, PhD: “In the health care industry in general, small sizes are typically based on Caucasian males, so once you get to women who truly have smaller frames there are no products available for them.”
Arjun Srinivasan, MD: “There’s a lot of potential for synergy between the infection prevention program and the antibiotic stewardship program.”

Sharon Ward-Fore, MS, MT(ASCP), CIC: "We’ve learned the hard way that restaurants, office settings, hair salons, fitness centers, and schools have really suffered for the lack of guidance by professionals like infection preventionists."

Abby Basalely, MD: “The majority of children will recover from MIS-C and we see them thriving and doing well post hospitalization if they need hospitalization for the syndrome.”
Tanya Lewis, CRCST: “I just think that infection preventionists and sterile processors should always work as a team. It should always be a team effort. It’s not them or us. It’s not sterile processing. It’s not infection prevention, but it’s us as a team. And that’s the way we’re going to keep our patients safe.”

Linda S. Estep, BS MT (ASCP), CIC: “I’ve done many hand hygiene audits in my day, I still do hand hygiene audits, when I’m in the hospitals now. If they know who you are, they scatter. They know the infection preventionists.”

Linda Spaulding RN, BC, CIC, CHEC, CHOP: “There have been 3,104,010 cases of COVID-19 among kids between the ages of zero and 20…. That means that 13.1% of all the cases of COVID-19 that we’ve seen in the US have been children.”
Kelly Cawcutt, MD, MS, FACP, FIDSA: “In a perfect world, vascular access teams and infection prevention teams really should be working very tightly together to optimize the practice of putting our vascular access in place.”

Daniel Burnett, MD, MBA: “The aerosols, the things that are the true danger and that can hang in the air for hours, depending on their size, are still released around the edges and around the nose of cloth masks. A cloth mask does very little to protect you.”
Rebecca Leach, RN, BSN, MPH, CIC: “The flu vaccine is mandated where I work. I do see a day where the COVID-19 vaccine will be mandated as well in health care facilities especially if—as we expect—COVID is not going away.”

Kevin Kavanagh, MD: “Throughout the history of evolution, and even through the history of mankind, you’ve seen species get wiped out. You’ve seen civilizations of man fall because of infections. And the thing that differentiates us from a tadpole is our science and our knowledge. And if we don’t take advantage of that….”

Linda Spaulding RN, BC, CIC, CHEC, CHOP: “Now the new challenge is going to be will we get definitive answers that the COVID tests that we’re currently doing will pick this variant up?”
Ann Marie Pettis, RN, BSN, CIC, FAPIC: “COVID-19 just never seems to let up. And every time you think you might be making a little bit of progress, some new thing comes along, like right now with potential resistance because of mutations. You can never let your guard down.”

Caitlin Stowe MPH, CPH, CIC: “There’s still a lot we don’t know about SARS-CoV-2 and the direct mechanisms of transmission…. It can be aerosolized. However, there is evidence of indirect transmission from surfaces to people.”

Kevin Kavanagh, MD: “If we keep spreading this virus around, it’s going to slowly devastate both our population and our economy.”
Mary Jean Ricci MSN, RNBC: “[Infection preventionists] really need to think about how we’re getting people from the assessment area to the vaccination area to the evaluation area in a unidirectional flow so that we don’t have the spread of the virus at the time of inoculation.”
Sharon Ward-Fore, MS, MT(ASCP), CIC: “Infection preventionists need to remind people to be vigilant both in health care and outside of health care. Because we’re not done with this yet. We have a long way to go before we’re fully protected.”

Too often the tracking of the use and disinfection is done with pen and paper. That's what leads to problems, says Michael Cousin.
Anthony Harris, MD, MBA, MPH: “There are a number of ways that [infection preventionists] are going to continue to be on the frontlines helping us fully understand the impact of COVID-19 and get to the other side of it.”
Devin Jopp, EdD, MS: “I think from sports teams to hospitality to construction sites, to many, many more, the infection prevention field will absolutely be bulging.”
Linda Spaulding RN, BC, CIC, CHEC, CHOP: “There’s not enough literature out there yet to say that once you get the vaccine, you won’t get COVID again, and the literature that is out there says that once you get the vaccine, even if you don’t get COVID again, you can still be an asymptomatic carrier.”

Cedric Steiner: “But the nursing home…. One could make an argument that [infection control is] more important there in some ways, because you have those residents in smaller spaces."
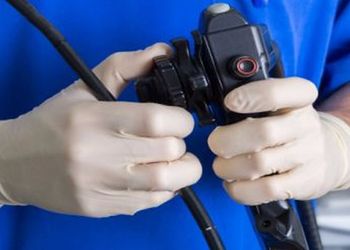
Linda Spaulding RN, BC, CIC, CHEC, CHOP: “Infection preventionists need to learn how to clean an endoscope, or at least observe the cleaning…. Infection preventionists need to make rounds, they need to talk to the person processing.”